
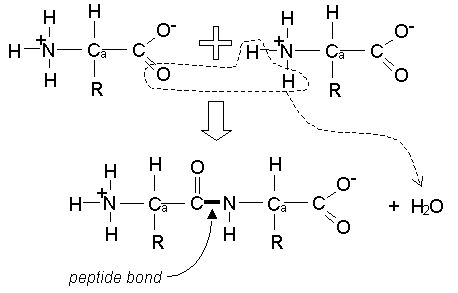
When the sequence of amino acids join together then it forms a monomer. They, as observed typically, are 5 or 6 carbon ring structures. They are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and exist in a ring structure. Saccharides are simple sugars that are linked by glycosidic linkage. Protein structure is divided into four different types primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. When various molecules of monosaccharides join together through glycosidic linkage then it forms a polysaccharides structure. When two simple units of sugars are joined together through glycosidic linkage then it forms a Disaccharide.

Monosaccharides are simple sugars with one water molecule attached to the carbon molecule. It is also formed by the process of condensation and can be broken down by hydrolysis. Amino acids are the structural units (monomers) that make up proteins. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N). It is formed by the process of condensation and can be broken down by hydrolysis. Amino Acids: Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (NH 2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. They are also composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. They are composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. They constitute repeating units of amino acids. They constitute repeating units of carbohydrates or monosaccharides. They are the building blocks of the body. They are the essential elements of the body that give energy to the body. Knowing this, we can deduce the correct answer to this question.They are the most important and useful carbohydrates found in the body. Makes it easier to store as it does not interfere with the balance of water in They can then convert glucose into a large, insoluble polymer called starch, which If the amine and carboxylic acid functional groups in amino acids join together to form amide bonds, a chain of amino acid units, called a peptide.

Many plants produce their own sugars in the form of glucose through the process of Glucose is a small, simple sugar molecule. So, these cannot be the monomer subunits of starch either. Cellulose and glycogen are also carbohydrate polymers made of many repeating units of Starch is a large carbohydrate made of many repeating units of a much smallerĪmino acids are the monomers of proteins, not carbohydrates. When various molecules of monosaccharides join together through glycosidic linkage then it forms a polysaccharides structure.
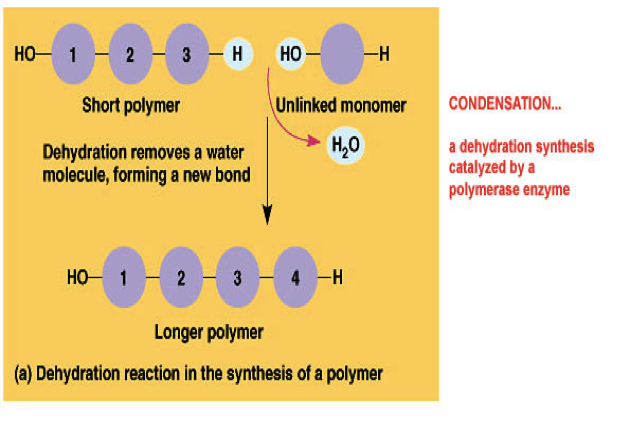
Means many, referring to the fact that polymers are made up of many repeating So, the monomer will be the amino acids, and the polymer will be the proteins themselves. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which contain elements such as H,N,O,C, and more. The word “monomer” contains the word mono- which means one, while the prefix poly- A monomer is a single molecule that can be joined together with other same molecules to form a polymer. Starch is a polymer made up of many monomers. A large molecule, starch, is formed from multiple smaller molecules. This question presents us with an example of an anabolic reaction. The formation of these bonds requires an input of energy, which is supplied by In contrast, anabolic reactions form bonds between small molecules, joining them Stored in cells in the high-energy bonds of a molecule called ATP so it can beĮasily accessed when needed. The breaking of bonds in catabolic processes releases energy, which is temporarily You might have learned that metabolic reactions can be grouped into those that areĬatabolic reactions are those that break the bonds in large, complex molecules,īreaking these molecules down into smaller subunits. Metabolism describes all of the chemical reactions that occur within living organisms This question asks us about a metabolic reaction, in which smaller molecules are Which monomer subunits join together to form starch in a metabolic reaction? (A) Glucose, (B) glycogen, (C) cellulose, or (D) amino acids. In some metabolic reactions, large molecules are made from smaller ones, as shown in


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
